Explain Different Types of Covalent Bond
The polar covalent character of water allows its molecules to become attracted to many other different types of molecules and disrupt their pre-existing bonds. Following are some points that can help to explain the stability of resonance structures.
2 1i Covalent Bonds And Other Bonds And Interactions Biology Libretexts
Metallic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that arises from the electrostatic attractive force between conduction electrons in the form of an electron cloud of delocalized electrons and positively charged metal ionsIt may be described as the sharing of free electrons among a structure of positively charged ions Metallic bonding accounts for many physical properties.
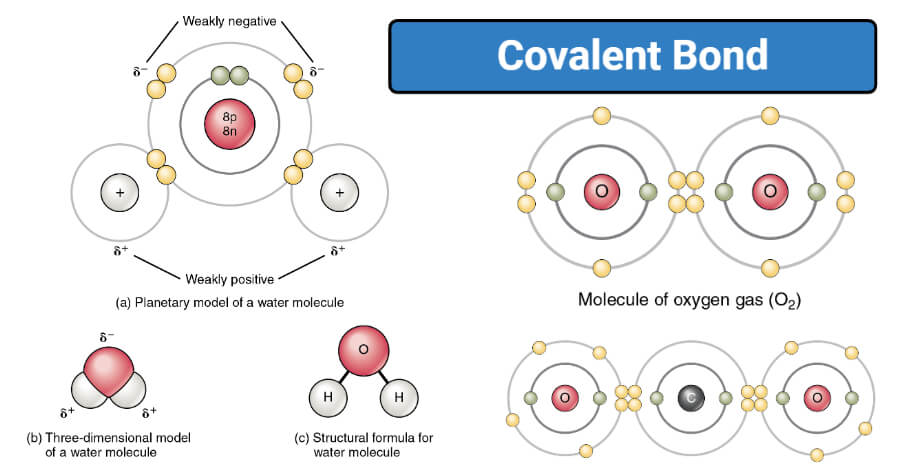
. Learn about trends in the. In the F 2 molecule the FF latex sigmalatex covalent bond is formed by the overlap of p z orbitals of the two F atoms each containing an unpaired electron. In a single bond the atoms share one pair of electrons which forms the link between the atoms.
The shred electrons are more likely to be near the atom whose electronegativity is higher. Since there are two O-H bonds in water their bond dipoles will interact and may result in. Full discussions of the topics covered by these problems are available in the Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry.
This interactive activity from ChemThink describes covalent bondinga type of chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons. The following button will activate a random display of problems concerning the reactivity of common functional groups. Bonds are formed by releasing energy which means a molecule.
A molecule which has one or more polar covalent bonds may have a dipole moment as a result of the accumulated bond dipoles. Which results in a single bond being a covalent bond. The octet rule is a chemical rule that generalizes that atoms of low atomic number 20 will combine in a way that results in their having 8 electrons.
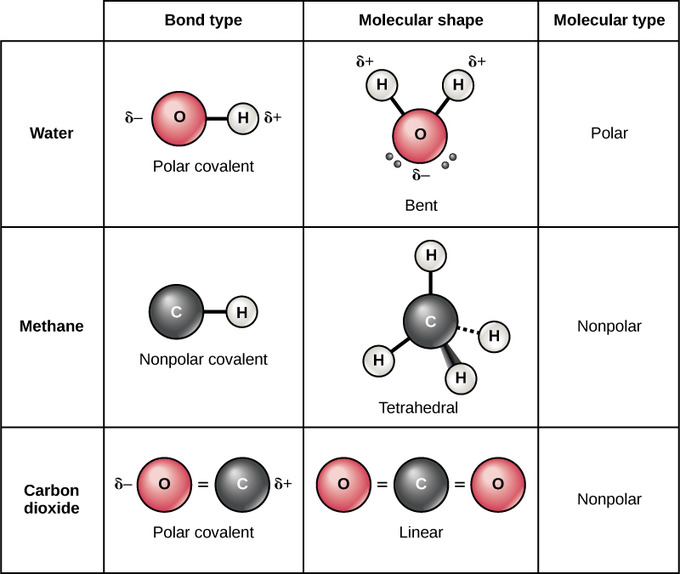
Single bonds are a type of covalent bond formed from the sharing of two electrons between two atoms one electron. An example is water. Lets look at three different types of covalent bonds.
The hybridization concept explains the formation of identical 4 C-H bonds and the tetrahedral shape of the molecule. An ionic bond is a type of chemical bond in which the atoms have different electronegativity values from each other. Investigate the attractive and repulsive forces that act on atomic particles and how the sharing of electrons can keep atoms together.
On the other hand a polar covalent bond is a covalent bond in which the shared electrons are more attracted to one of the atoms than the other. A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds. For a covalent molecule AB the bond length is given by d r a r b.
A chemical bond that is formed from the sharing of two electrons between two atoms. Examples of Covalent Bond. In the kinetic theory of gases the.
See how two hydrogen atoms interact with each other to create a covalent bond. In a covalent compound it is the sum of their covalent radii. Explain the difference using the octet rule.
Depending on context the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. Thus the valence theory doesnt explain the covalent bond of the methane molecule. What are some differences between an ionic bond and a covalent bond.
Since the nature of the overlapping. According to this concept when a carbon atom reacts with a hydrogen atom. These cases of electron sharing can be predicted by the octet rule.
However it is important to note that the bond formed between two individual water molecules is a hydrogen bond and not covalent. The diboron bond which is a pi bond is an. A single bond can also be stated as a sigma bond.
A non-polar covalent bond is a bond where the shared electrons are shared equally. For example sodium Na and chlorine Cl form an ionic bond to make NaCl table salt. The most significant contribution is from the structure with the most covalent bonds.
However in a covalent bond the atoms are bound to share electrons. It is determined experimentally by x-ray diffraction or electron diffraction method or spectroscopic method. A single bond is a chemical bond between two atoms that involves two valence electrons in chemistry.
The bond length in chemical bonding is the sum of their ionic radii in an ionic compound. Due to the identical resonance structures equal energy each resonance hybrid contributes equally. In the case of water we know that the O-H covalent bond is polar due to the different electronegativities of hydrogen and oxygen.
The Three Covalent Bonds. This theory is used to explain the covalent bond formation in many molecules. In quantum physics organic chemistry and biochemistry the distinction from ions is dropped and molecule is often used when referring to polyatomic ions.
Give some specific examples of substances that contain ionic or covalent bond. For example if we talk about water H2O it is a polar covalent bond. First described by Gilbert Lewis a covalent bond occurs when electrons of different atoms are shared between the two atoms.
There are different types of hybridization-based on the mixing of the orbitals. Sugar is a carbohydrate compound that is composed of 12 carbon atoms.

Covalent Bond Definition Types And Examples

Covalent Bond Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock

Notes 5 3 Covalent Bonds Covalent Bond A Force That Bonds Two Atoms Together By A Sharing Of Electrons Each Pair Of Shared Electrons Creates Ppt Download
Comments
Post a Comment